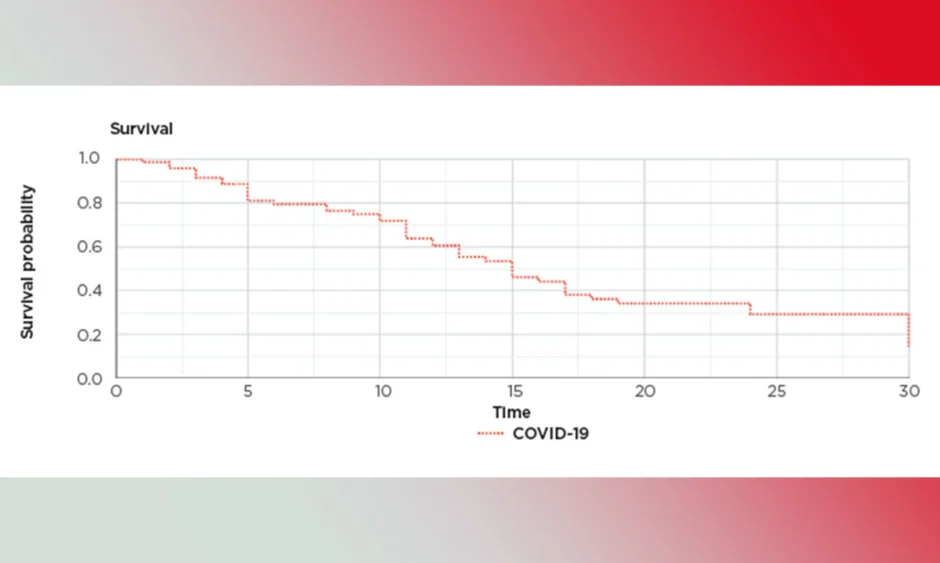
COVID-19 took the world by storm, quickly growing into a global pandemic, and causing many countries to go on lockdown. Two years later, the virus is spreading, but not with the same intensity as before, thanks to vaccinations and proper preventative techniques. Nevertheless, the COVID-19 virus has undergone numerous variations and mutations, some more contagious than others, whereas others cause more serious illnesses. While studying the different mutations, experts in public health have discovered various covid-19 Avenel risk factors. Continue reading to learn more.
- Advanced age
As you age, the immune system, like numerous other body systems, starts to lose effectiveness. Your immune system might respond more slowly or provide weaker responses than it formerly did. You could also suffer from an autoimmune disorder. While the age at which these changes occur differs, research shows a higher risk of serious COVID-19 symptoms in older people than in teens and young adults.
- Weakened Immunity
Your immunity is the protector when it comes to safeguarding you from infection. This system is accountable for spotting and guarding against viruses, bacteria, and other foreign materials than invade the body.
Your immunity could be inherently weak due to illnesses like HIV, autoimmune disease, or medically weakened by treatments like chemotherapy, steroids, or antidepressants. If so, your immune system might not effectively identify or kill the virus causing COVID-19.
- Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the body undergoes numerous changes. Pregnancy has some effect on every bodily system, including immunity. Women who are pregnant or have recently delivered are at greater risk of developing a severe COVID-19 infection.
- Blood Disorders
Your blood is a huge player in your immune system. Blood hosts the white blood cells, and other immune cells circulate throughout the body to identify and combat infections. COVID-19 can heighten the risk of blood clots and other health complications. Individuals with blood clotting disorders like anemia, leukocytosis, sickle cell anemia, and more could be more vulnerable to serious COVID-19 infections.
- Cancer
Cancer is the umbrella term for numerous diseases wherein rapidly dividing cancer cells overwhelm healthy tissue and cells. Once this occurs, cancer cells keep the impacted body part from functioning normally, resulting in various symptoms.
Specific cancers, such as leukemia, could directly weaken the immune system and increase the risk of COVID-19 infection. Moreover, cancer treatments like radiation and chemotherapy can efficiently eliminate cancer cells, but at the same time, destroy immune cells, making you susceptible to infections.
- Diabetes
Type I disease is an autoimmune disease that impairs the pancreas, the organ that helps regulate blood sugar by generating insulin. Type II diabetes is often acquired due to lifestyle factors, such as nutrition. While both conditions could raise susceptibility to COVID-19, type 1 diabetes bears a greater risk factor.
- Lifestyle Factors
Different lifestyle factors are associated with more serious COVID-19 infection. These habits could result in health disorders that are often well-known. Common lifestyle factors associated with COVID-19 include substance abuse, sedentary living, smoking, or poor dieting.
Serious COVID-19 infections can develop in individuals without identifiable health concerns, including children and young adults. However, persons with the above conditions are more vulnerable to severe or life-threatening infection. As such, everybody must take precautions to avoid the spread of the virus to safeguard persons in these high-risk groups. Vaccination against COVID-19, regular and thorough hand-washing, mask-wearing, self-quarantines, and other measures can reduce the risk for everyone. Nonetheless, consult a specialist if you identify any warning signs of COVID-19, be it difficulty breathing, sore throat, fatigue, or more.