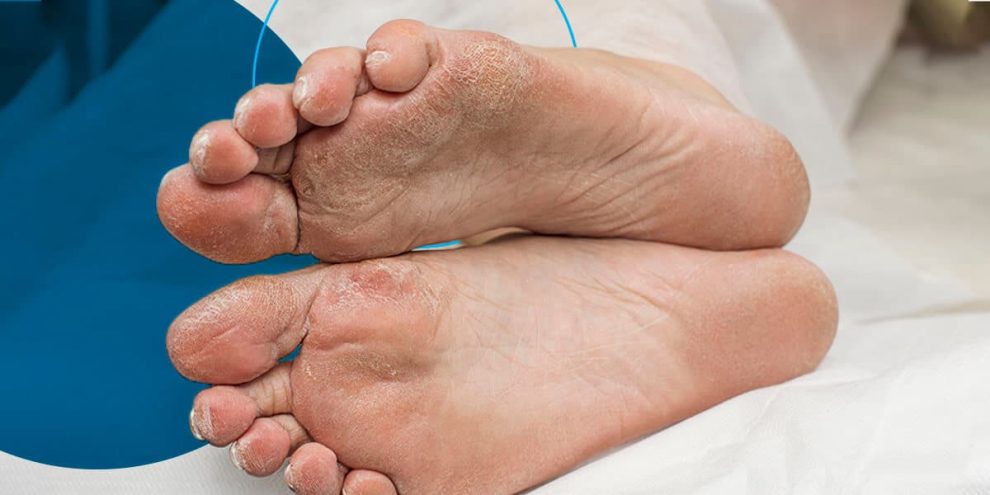
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs either when there is not enough insulin produced or if your body cannot use the insulin, leading to increased blood sugar levels. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to several other medical complications, such as diabetic feet.
Newnan diabetic feet management includes comprehensive care and customized treatments to relieve the symptoms.
Understanding diabetic feet
Diabetic feet are a group of foot-related health problems caused by diabetes. It may lead to sores, deformities, and infections in your feet.
If not treated quickly, this may lead to complications like ulcers and gangrene. Sometimes it may be so several, that your surgeon may even amputate your toe, foot, or even a part of your leg to prevent the spread of the infection.
Risk factors
There are several factors that can increase your likelihood of developing diabetic feet, such as:
- Compromised blood flow to the feet
- Trouble managing your blood sugar
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- A BMI of more than 25 (obesity)
- Hypertension
- High cholesterol
Clinical features of diabetic feet
The signs of diabetic foot may include:
- Pain
- Numbness
- Tingling or stinging sensation
- Skin discoloration
- Loss of sensitivity to hot and cold
- Loss of hair in the affected area
- Swelling around your feet
- Blisters and ulcers
- If infected it can lead to foul-smelling pus discharge
Diagnostic tools for diabetic feet
To diagnose diabetic feet, your doctor will:
- Review your medical history about diabetes, its symptoms and how well it has been managed
- Physically examine your feet to check for swelling, skin discoloration, numbness, and pus discharge
- Order imaging tests like X-rays to rule out any bone involvement
- Consider a biopsy test to determine the underlying cause of infection to help guide the treatment
Treatment options for diabetic feet
Diabetic feet treatment is provided by a podiatrist (foot specialist), which may include lifestyle changes and a conservative approach, such as:
- Taking your diabetes medication regularly to control it
- Checking your feet for any changes
- Getting a podiatry examination at least once a year
- Maintaining good blood circulation to your feet
- Practicing good personal hygiene methods such as cleaning your feet regularly
- Quit smoking
- Avoid moving around barefoot
- Wearing socks and shoes all the time
For severe cases of diabetic feet that do not respond to the above approaches due to infection, your doctor may recommend oral or IV (intravenous) antibiotics.
Remember
You are at an increased risk of ulcers and infections in your feet if you are diabetic. It is important to keep a check on your blood sugar levels and care for your feet every day. Also, keep a check on the skin changes since early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent hospitalization, deformity, and amputation.