Heart problems are one of the most severe conditions that may affect your body. Your heart is responsible for blood transfer, thus transporting nutrients and waste throughout your body. This means its functions are necessary for your body’s health, and problems may be fatal. However, despite the fragility of the issues in your heart, treatment solutions are available. Treatment options like pacemaker Houston have emerged in recent times. More about pacemakers and how they function are discussed below in detail.
What is a Pacemaker?
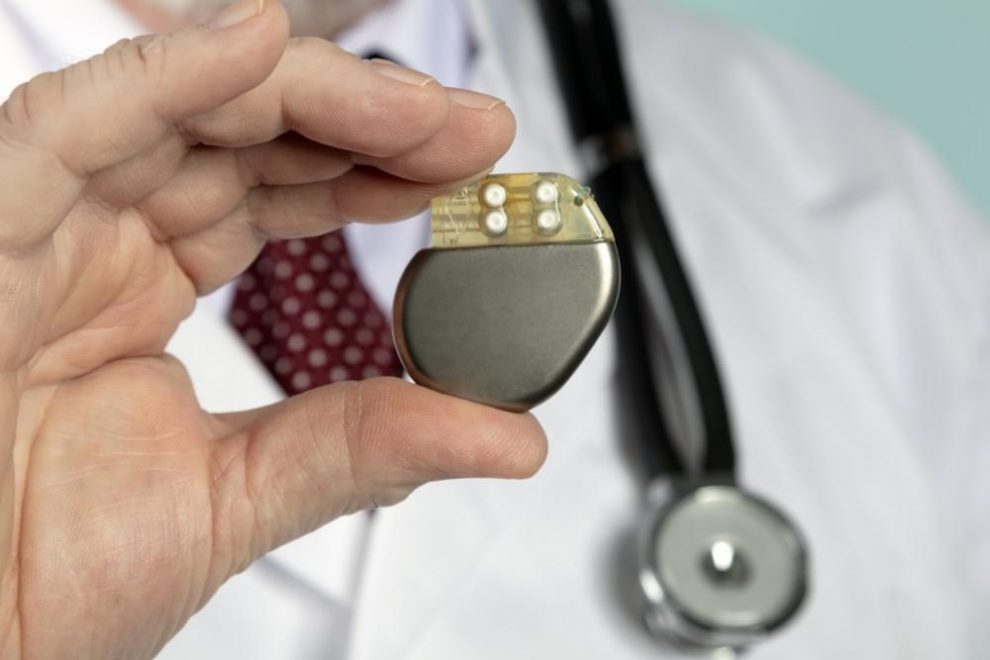
This is a tiny device implanted into your chest to assist in controlling your heartbeat. A surgical procedure is performed, thus preventing your heart from beating too slowly.
Since a pacemaker works to control your heartbeat, your physician may recommend a temporary or permanent pacemaker, depending on the requirements.
A temporary pacemaker is used if you have a slow heartbeat following a surgery, medication overdose, or heart attack, although your normal heartbeat is expected to return.
On the other hand, a permanent pacemaker is implanted to correct an irregular heartbeat that is chronically slow and help treat heart failure.
How a Pacemaker works
The chambers of your heart work together with the heart’s electrical system to maintain a standard heartbeat rate. The heart’s electrical system begins at the sinus node when controlling your heartbeat.
The pacemaker can correct slow heartbeat rates by sending electrical signals to the heart. Some newer pacemakers have breathing rates and body motion sensors to identify increased heart rates when exercising.
A pacemaker can be referred to as a cardiac pacing device and is of various types, including:
- Single chamber pacemaker that transports electrical impulses to the right ventricle of the heart
- Dual-chamber pacemaker to transport electrical impulses to your right atrium and ventricle of the heart to assist in the control of the timing of contractions between the two sites
- A biventricular pacemaker is typically for people with heartbeat problems and heart failure. This pacemaker stimulates both lower heart chambers for efficient heart beating.
A pacemaker has two main parts known as:
- Lead electrodes – They vary from one to three insulated flexible wires placed in different heart chambers to deliver electrical pulses that adjust the heart rate. Newer leadless pacemakers have emerged and can be placed directly into the heart muscle.
- Pulse Generator – This is a tiny metal enclosure housing the battery and the electrical circuitry that enables the control of the rate of electrical pulses being sent to your heart
Various risk factors associated with pacemaker implantation may include:
- Swelling, bleeding, or bruising at the site of the pacemakers if you take blood thinners
- Infection near the area where the device is put
- Damage to nerves or blood vessels close to the pacemaker
- Blood clots in the surrounding areas
- Blood in the area between the chest wall and lung
- Collapsed lung
- Shifting of the leads or device’s position causes cardiac perforation
Heart problems are dealt with great care as any mishaps during procedures may be fatal. Heart problems are severe and require immediate medical attention. For more pacemaker inquiries, call our offices in Houston, TX.